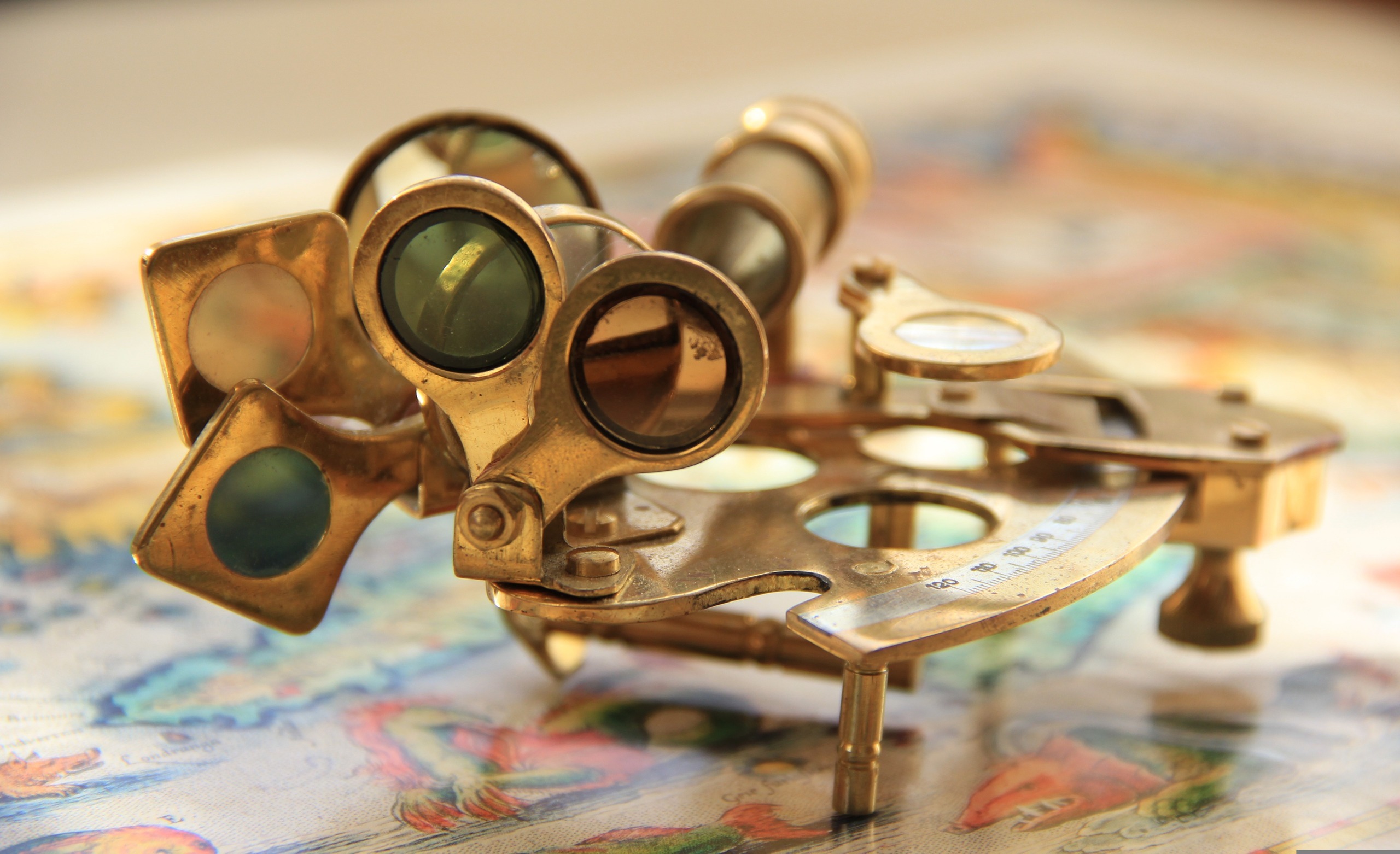

How To Use The Sextant
Whether you’re an aspiring sailor or simply curious about navigation techniques, understanding how to use the sextant opens up new horizons—literally! Navigating the vast oceans has always sparked a sense of adventure and wonder. For centuries, sailors relied on celestial navigation to chart their courses.
One indispensable tool in this age-old practice is the sextant. With its elegant design and precise functionality, the sextant not only serves as a navigational instrument but also embodies humanity’s quest for exploration.
If you’ve ever gazed at the stars and wondered how ancient mariners found their way across uncharted waters, then learning how to use a sextant can unlock secrets of maritime history. This remarkable device allows you to measure angles between celestial bodies and horizon lines with incredible accuracy.
Join us as we dive into the fascinating world of sextants: from their historical significance to practical steps for mastering this timeless skill.
The History and Importance of Sextants
The sextant has a rich history that dates back to the 18th century, emerging as one of the most crucial navigational tools for sailors. Invented by John Hadley and Thomas Godfrey, this remarkable instrument transformed maritime navigation.
Before its invention, celestial navigation relied heavily on less accurate methods. The sextant allowed mariners to measure angles between celestial bodies and the horizon with unprecedented precision. This advancement was vital for long voyages across uncharted waters.
Its importance cannot be overstated. By providing reliable means of determining latitude and longitude, sextants enabled explorers to confidently traverse vast oceans. They opened up new trade routes and facilitated global exploration, shaping world history in profound ways.
Even today, while technology has shifted towards GPS systems, the principles behind the sextant remain foundational in navigation courses worldwide. Its legacy endures as a symbol of human ingenuity in conquering the seas.
How a Sextant Works
A sextant is an ingenious navigational instrument that measures the angle between a celestial object and the horizon. This measurement helps determine your latitude and longitude at sea or on land. When using a sextant, light from the celestial body—like the sun or stars—is reflected off a mirror.
The user aligns this image with the horizon through another mirror. As you adjust for clarity, you’re effectively creating a precise angle measurement. This angular data is crucial for navigation. By knowing your position relative to specific stars, mariners can plot their course accurately on nautical charts.
The mechanics of a sextant involve not just mirrors but also finely calibrated scales and telescopes for precision sighting. Each component plays its part in ensuring navigators can trust their readings amidst changing conditions at sea or in remote locations.
Components of a Sextant
A sextant is made up of several key components that work in harmony to help navigators measure angles accurately. At its core, the frame holds everything together, providing stability and structure. The index arm moves along an arc and plays a crucial role in measuring angles.
It’s attached to the micrometer drum for fine adjustments—a feature that enhances precision. Another important part is the telescope. This allows users to sight celestial bodies while maintaining alignment with their horizon reference point. The optics must be clear for accurate readings.
Additionally, there are vernier scales on the instrument that help read measurements down to minutes or seconds, greatly improving accuracy. A spirit level ensures the sextant remains horizontal during use. Proper calibration of these components can make all the difference in navigation at sea or during exploration.
How to Use a Sextant: Step by Step Guide
Using a sextant might seem daunting, but it’s quite manageable with practice. This is a necessary skill if you want to navigate on the open ocean or are interested in astrology. So let’s go ahead and start navigating our world.
Step #1: Preparing the Sextant and Sighting Objects
Before you embark on your celestial navigation journey, ensure your sextant is in top shape. Check that the index arm moves smoothly across the arc and that all screws are tightened. A well-maintained instrument will yield more accurate results.
Next, select a reliable sighting object. Common choices include the sun during midday or prominent stars at night. Make sure there’s minimal obstruction to your line of sight for optimal accuracy.
Align yourself comfortably with the sextant held steady in one hand while using the other to adjust its angle. This balance is crucial as any movement can affect readings significantly.
As you prepare to take measurements, keep an eye on external factors like weather conditions and sea state. Fluctuating elements can impact visibility and clarity when sighting objects in the sky or horizon.
Step #2: Taking Measurements and Calculating Angles
Once you’ve set your sextant and have your sighting objects prepared, it’s time to take measurements. Position the sextant so that the horizon is visible through the telescope.
Carefully adjust the index arm until you see the object in view. Align it with the horizon by moving the micrometer knob. This process requires patience and a steady hand; even minor movements can lead to inaccuracies.
After achieving alignment, read off the angle displayed on the scale. Make sure to note this reading accurately as it will be crucial for later calculations.
Next comes calculating angles, which involves understanding nautical terms such as “altitude” — how high an object appears above sea level. Use trigonometric functions or tables if necessary, especially when dealing with various celestial bodies like stars or planets.
Precision here lays down a strong foundation for navigation accuracy in subsequent steps.
Step #3: Correcting for Errors and Obtaining an Accurate Reading
After taking your initial readings, it’s crucial to account for potential errors. Several factors can affect accuracy, including atmospheric conditions and the observer’s position.
Start by checking the index error, which occurs when the sextant’s zero point is not aligned with true zero. To do this, bring a horizontal line of sight into view and see if it aligns perfectly at zero degrees. If not, make adjustments accordingly.
Next, consider refraction. This optical phenomenon occurs due to light bending in different air densities. Consult nautical tables or use correction formulas specific to your latitude.
Apply any necessary corrections based on time and location data from reliable sources such as almanacs or GPS systems. Remember that even small discrepancies can lead to significant navigation errors over long distances. Take your time and ensure every reading reflects careful consideration of these variables.
Tips for Accurate Readings
To achieve accurate readings with a sextant, start by ensuring that the instrument is properly calibrated. Regular checks can prevent errors due to misalignment or mechanical issues. Next, always use a stable platform for measurement.
Whether on a boat or docked, avoid any movement that might affect your reading. A steady hand significantly improves accuracy. Consider environmental factors as well. Bright sunlight can create glare; therefore, employing a sunshade helps maintain clear visibility when sighting objects.
When taking measurements, repeat the process multiple times and average your results. This practice minimizes random errors and enhances reliability. Keep notes during each measurement session. Documenting conditions like time and weather allows for better context when analyzing data later on.
Common Mistakes to Avoid When Using a Sextant
One of the most frequent errors is not ensuring a stable horizon. A bumpy sea or an unstable platform can skew readings significantly. Always find a steady spot to minimize fluctuations. Another mistake revolves around improper calibration.
Failing to calibrate your sextant before use can lead to inaccurate measurements. Regularly check and adjust for this vital step. Additionally, overlooking corrections for atmospheric refraction can affect results as well. The atmosphere bends light, which may mislead your angle readings if neglected.
Many users also rush through sighting instead of taking their time with proper alignment. Precision matters when aiming at celestial objects; patience is key. Neglecting record-keeping often leads to confusion later. Document each measurement meticulously to avoid discrepancies during calculations or comparisons later on in navigation tasks.
Real-Life Applications and Examples
Sextants have played a crucial role in maritime navigation for centuries. Sailors relied on these instruments to determine their position at sea, ensuring safe passage through uncharted waters. In modern times, the sextant still finds its place among navigators and sailing enthusiasts who value traditional techniques.
For instance, during long ocean voyages or regattas, sailors often use sextants as a backup method when electronic systems fail. A notable example is the famous voyage of Sir Francis Chichester in 1967. He circumnavigated the globe solo using celestial navigation with a sextant, showcasing its reliability even without contemporary technology.
Additionally, educational institutions teach students about astronomy and navigation principles through hands-on experiences with sextants. This fosters an appreciation for historical practices while developing practical skills that remain relevant today.
Conclusion: The Beauty and Necessity of the Sextant
The sextant remains a fascinating instrument that blends art and science. Its design reflects the ingenuity of human thought, bridging centuries of exploration and navigation. With its elegant mechanics, the sextant has not only charted seas but also captured the imaginations of sailors, astronomers, and adventurers alike.
This tool embodies precision in an era where technology often overshadows traditional methods. Mastering how to use the sextant opens up a world steeped in history while offering practical skills for modern-day navigation. It reminds us that even in our fast-paced digital age, there exists beauty in simplicity and reliability.
Understanding this ancient device can deepen your appreciation for navigation itself—an essential skill for anyone who loves exploring uncharted waters or hiking through rugged terrains. By embracing both its challenges and rewards, you connect with generations past who have relied on this remarkable tool to guide their journeys across vast oceans.
The journey into learning how to use the sextant is not merely about acquiring technical knowledge; it’s about recognizing a profound link between humanity’s quest for exploration and nature’s boundless horizons. This connection enriches every adventure you undertake, whether you’re setting sail on distant seas or simply gazing at stars from your backyard.



Till now I never knew what a sextant was, can you answer these questions I have about a sextant ?
What was the most challenging part for you in learning how to use a sextant, and how did you overcome it?
Do you think the sextant still holds importance in modern navigation, or has technology made it obsolete?
Have you tried applying the sextant techniques in real-world navigation? How accurate were your results?
What tips or tricks would you share for beginners struggling with sextant readings?
Hey Jr,
Thanks for stopping by today. The challenging part of learning to use a sextant is learning how and why it works. Once you learn the basics, everything else falls into place. The short answer to your second question is yes. The sextant works just as well today as it did for ancient sailors so even though technology has made it easier to navigate, it hasn’t made the sextant obsolete.
I have not used my sextant for navigation in a real world situation yet but I do go out on a clear night sky and practice. Astrologists use sextants as well and it makes for good practice when you are not navigating. Remember, the only way to become proficient using a sextant is practice, practice and more practice.
Once I learned what I was doing, my reading became more accurate. The biggest tip I cannot suggest is to buy a guide on how to use a sextant and find someone who knows how to use one and learn from them. Lucky for me, my best friend is a boat captain and he was kind enough to teach me how to properly use a sextant.
I hope I was able to answers your questions in a way that will help you get started. Go ahead and begin your journey into this extraordinary way of navigating using the stars the same way our forefathers did when they were exploring the world and discovering the places we live today.
Best wishes Jr,